Open 7 days
- Mon - Fri 8am-8pm
- Sat 8am-12pm
- Sun 8am-12pm
After hours veterinary care
After hours veterinary care
Hip Dysplasia (HD) is a genetic disease passed from the sire or dam.
What is interesting is that the puppy is born with a completely normal hip (but is a genetic carrier of the disease that will manifest itself during development).
At approximatelt two weeks of age, the ligaments that hold the femoral head in the acetabulum (ie the ligaments that hold the ball joint in the socket) become weak and loosen.
The femoral head (ball joint) no longer fits snugly in the joint. It loosens. The femoral head “rattles around” in the socket due to the laxity.
Juvenile bones are very soft. They form under the physical forces that they are placed under during development.
The femoral head runs around the edge of the acetabulum, a bit like a backet ball rimming the hoop. Since the femoral head is loose and putting pressure on the edge of the acetablum, the acetabulum becomes very shallow. The femoral head becomes quite mushroom shaped instead of spherical. This gives rise to an abnormal development called hip dysplasia. The joint is misshapen and the laxity and mushrooming of the femoral head leads to severe degenerative joint disease progressing to osteoarthritis with time.
This causes chronic pain.
JPS is a procedure that is designed to correct this abnormality during development. The challenge is to diagnose a problem during the small window of opportunity between 12-16 weeks of age.
Juvenile Pubic Symphysiodesis is a procedure to correct laxity during the anatomical growth of the hip.
This image shows a developing hip in a 12 week puppy that has joint laxity. The hip can be seen to be quite loose in the joint. This laxity is the pathogenesis for the development of a misshapen hip joint and degenerative joint disease.
During development of the pelvis, the pubic symphsis is soft cartilage. By cauterising the cranial portion of the pubic symphysis, it causes this growth plate to close early. This anchors the centre of the pelvis causing it to curve slightly as it grows and expands. This pushes the ball joint back into the socket and reduces the deformity of the developing femoral head and acetabulum.
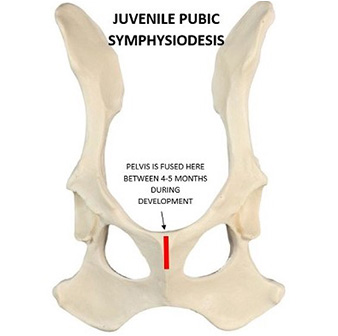
The diagram above shows where the pubic symphysis is cauterised during development. This procedure has a very low morbidity and complication rate. The young puppies bounce back very quickly and the next day you would not know they had surgery. There is minimal pain and post operative swelling. It is done through a small hole for exposure to the ventral pubic bones.
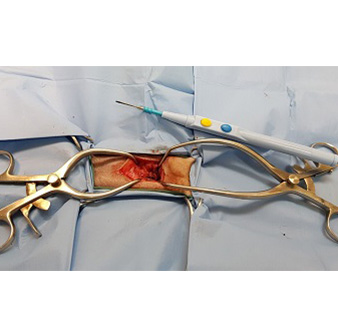
The exposure is small and atraumatic. Cautery is used to fuse the pubic symphysis.
At Treendale Pet Medical we offer an after hours care on Bunbury and after hours care on Eaton with world class operating facilities and equipment.
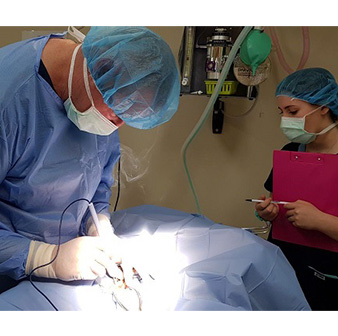
Dr Rob Hill is performing a Juvenile Pubic Symphysiodesis in the operating theatre at Treendale Pet Medical near Bunbury.
Class IV laser is used post operatively to reduce pain and inflammation and halve healing time. At Treendale Pet Medical we have a K-Laser and laser therapy has been proven to vastly reduce healing time and reduced pain and inflammation causes less wound licking and risk of infection.
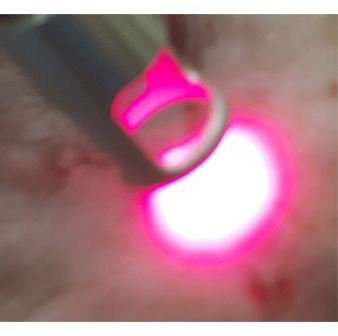
K-Laser in use to reduce post operative pain and inflammation and to speed up healing.
Nurse leticia is doing K-Laser therapy post operatively.
Treendale Pet Medical is a fear free veterinary hospital near Bunbury Western Australia. Our patient is getting executive care from our nursing team. The patient has had four kinds of analgesia and is having a very calm and pain free recovery. Our patient will have soft calming music to listen to as he recovers. He has a warmed cage, soft bedding, Adapatil and soft music. His recovery from surgery will be smooth and pain free.

Social distancing is easy for pets and people in our spacious waiting areas.



